
Are you interested in creating the perfect environment for your greenhouse? If so, you may be wondering about the optimal orientation to maximize sunlight and energy efficiency. In this article, we will explore the factors to consider when choosing the ideal orientation for your greenhouse. By understanding the impact of sunlight, wind, and seasonal variations, you’ll be able to make an informed decision that enhances the growth and wellbeing of your plants. So, let’s dive into the world of greenhouse orientation and unlock the secrets to a thriving garden.
Factors to Consider
When it comes to determining the optimal orientation for a greenhouse, there are several factors that you should consider. These factors can greatly impact the overall success and efficiency of your greenhouse operation. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can ensure that your greenhouse is positioned in the best possible way to take advantage of natural resources and provide the ideal growing conditions for your plants. The key factors to consider include sunlight exposure, wind direction, climate, terrain, existing structures, access and visibility.
Sunlight Exposure
Importance of Sunlight for Greenhouses
Sunlight plays a vital role in the growth and development of plants. It provides the necessary energy for photosynthesis, which is crucial for the production of food and nutrients. Therefore, ensuring that your greenhouse receives sufficient sunlight is essential for the health and productivity of your plants.
Optimal Sunlight Exposure for Greenhouses
To determine the optimal sunlight exposure for your greenhouse, you need to consider the specific requirements of the plants you will be growing. Some crops may thrive in full sun, while others may prefer partial shade. Understanding the sunlight needs of your plants will help you position your greenhouse in a way that maximizes sunlight exposure without causing overheating or sunburn.
Measuring Sunlight Exposure
There are various methods you can use to measure sunlight exposure in your greenhouse. One common method is to use a light meter, which can provide accurate readings of the intensity of sunlight. Another approach is to observe the patterns of sunlight throughout the day and year, taking note of any areas that may be shaded by nearby trees or buildings. Additionally, you can consult local weather data to determine average sunlight hours in your area.
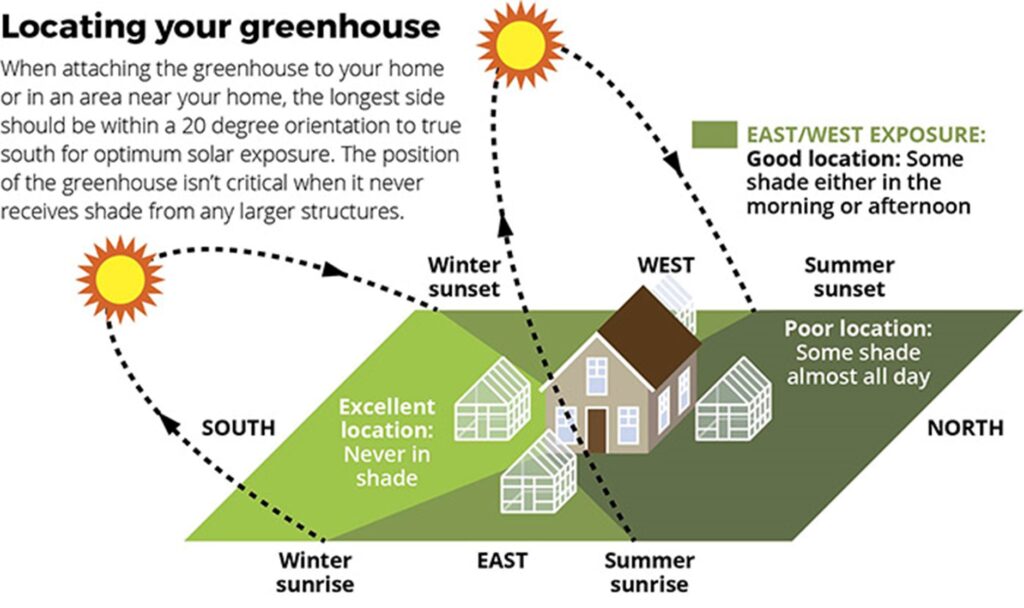
This image is property of sturdi-built.com.
Wind Direction
The Impact of Wind on Greenhouses
Wind can have both positive and negative effects on greenhouses. While gentle breezes can provide natural ventilation and help to prevent humidity buildup, strong winds can cause damage to structures and disrupt the delicate balance of temperature and humidity inside the greenhouse.
Protecting Greenhouses from Wind
To protect your greenhouse from strong winds, it is important to consider wind direction when determining its orientation. Positioning your greenhouse with the longest side facing away from prevailing winds can help minimize the effects of wind. Additionally, installing windbreaks such as fences or rows of trees can provide further protection and help maintain a more stable growing environment.
Determining Wind Direction
There are various methods you can use to determine the prevailing wind direction in your area. One simple approach is to observe the movement of vegetation or flags nearby, as they can indicate the direction of the wind. Additionally, consulting local weather data or talking to other growers in your region can provide valuable insights into wind patterns.
Climate
Understanding the Climate’s Effect on Greenhouses
The climate of your location plays a crucial role in determining the optimum orientation of your greenhouse. Different climates have varying levels of sunlight, temperature ranges, and precipitation, which can greatly impact plant growth and the overall performance of your greenhouse.
Choosing an Orientation for Different Climates
In warmer climates, it is beneficial to position the longest side of the greenhouse in an east-west direction. This allows for maximized sunlight exposure in the mornings and evenings while avoiding excessive heat buildup during the midday hours. In colder climates, positioning the longest side of the greenhouse in a north-south direction can help capture more sunlight during the winter months when the sun is lower in the sky.
Adapting to Extreme Climates
If you are located in an area with extreme climate conditions, such as high winds or frequent storms, it is essential to design your greenhouse with these factors in mind. Reinforced structures, sturdy glazing materials, and proper insulation can help withstand harsh weather conditions and maintain a stable environment for plant growth.
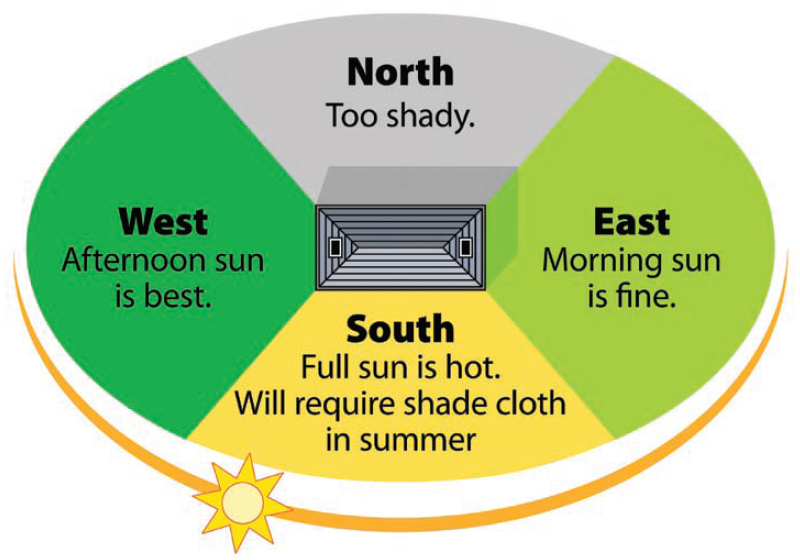
This image is property of arcadiaglasshouse.com.
Terrain
Considering Terrain for Greenhouse Orientation
The characteristics of the terrain surrounding your greenhouse can significantly impact its orientation and overall effectiveness. It is important to carefully evaluate factors such as slope, drainage, obstructions, shadows, and soil quality when determining the best position for your greenhouse.
Slope and Drainage
Positioning your greenhouse on a slope can have both advantages and disadvantages. While a sloped terrain can facilitate natural water drainage, excessive slopes can lead to uneven sunlight exposure and make construction more challenging. It is important to strike a balance that allows for proper drainage while maintaining a level enough surface for structural stability.
Obstructions and Shadows
Take note of any obstructions such as tall trees, buildings, or hills that may cast shadows over your greenhouse. Shadows can significantly reduce sunlight exposure and interfere with the growth of your plants. By carefully considering the surrounding landscape, you can position your greenhouse in a way that minimizes the impact of shadows and maximizes sunlight exposure throughout the day.
Soil Quality
Evaluate the quality of the soil in the area where you plan to build your greenhouse. The soil should be well-drained and rich in nutrients to support healthy plant growth. If the soil quality is poor, you may need to consider alternative options such as raised beds or container gardening to ensure optimal growing conditions for your crops.
Existing Structures
Working with Existing Structures
If you have existing structures on your property, such as outbuildings or trees, it is important to take them into account when determining the orientation of your greenhouse. Consider how these structures may impact sunlight exposure, wind patterns, and access to your greenhouse.
Compatibility of Orientation with Buildings
Ensure that the orientation of your greenhouse does not cause excessive shading or interfere with the functionality of existing buildings on your property. It is important to strike a balance that allows both the greenhouse and existing structures to coexist harmoniously.
Modifying Structures for Optimal Orientation
In some cases, you may need to make modifications to existing structures to achieve the optimal orientation for your greenhouse. This could involve trimming or removing trees, relocating buildings, or making adjustments to fences or walls. Consulting with professionals such as architects or engineers can help ensure that any modifications are done safely and effectively.

This image is property of extension.unh.edu.
Access and Visibility
Convenience and Accessibility
Consider the accessibility of your greenhouse when determining its orientation. Positioning it near a driveway or pathway can provide easy access for tending to your plants and transporting supplies. Additionally, ensure that the entrance to your greenhouse is easily accessible from your home or other key areas of your property.
Aesthetics and Visibility
The aesthetic appeal of your greenhouse can enhance the overall appearance of your property. Positioning your greenhouse in a visible location can showcase your gardening efforts and serve as an attractive focal point. Consider the visual impact of your greenhouse when choosing its orientation to ensure that it complements the overall landscape design.
Energy Efficiency
Maximizing Natural Heating
Choosing the optimal orientation for your greenhouse can greatly impact its energy efficiency. By positioning the longest side of the greenhouse to face the direction that receives the most sunlight, you can maximize natural heating and reduce the need for additional heating systems. This can result in significant energy savings and a reduced carbon footprint.
Optimizing Natural Ventilation
Proper airflow is essential for maintaining a healthy growing environment inside your greenhouse. By positioning your greenhouse in a way that takes advantage of prevailing winds, you can optimize natural ventilation and reduce the need for mechanical cooling systems. This not only helps maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels but also improves air circulation, reducing the risk of disease and pest infestation.
Reducing Energy Consumption
The orientation of your greenhouse can also impact energy consumption, particularly in relation to lighting and artificial heating or cooling systems. By maximizing natural sunlight exposure, you can reduce the need for artificial lighting during the day. Additionally, positioning your greenhouse to minimize heat loss during colder months can help reduce the reliance on heating systems. These energy-saving measures can result in lower operational costs and a more sustainable greenhouse operation.
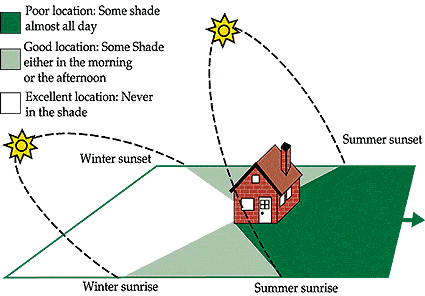
This image is property of greenhouseinfo.com.
Crop Compatibility
Considering Crop Requirements
Different crops have varying requirements in terms of sunlight, temperature, humidity, and overall growing conditions. When determining the orientation of your greenhouse, it is important to consider the specific needs of the crops you plan to grow. Some crops may thrive with more shade, while others require full sun exposure. Understanding these requirements will help you position your greenhouse in a way that provides the ideal growing conditions for your chosen crops.
Greenhouse Orientation for Different Crops
Depending on the requirements of your crops, you may need to adjust the orientation of your greenhouse. For example, crops that require more shade may benefit from a north-facing orientation, while those that need full sun exposure may require an east-west orientation. By carefully considering the needs of your crops, you can ensure that they receive the optimal amount of sunlight and other environmental factors needed for healthy growth.
Consulting Experts
Seeking Professional Advice
If you are unsure about the ideal orientation for your greenhouse or need guidance on how to navigate the various factors involved, it is highly recommended to seek professional advice. Consulting with experts such as architects, engineers, and agricultural specialists can provide valuable insights and help you make informed decisions. These professionals possess the knowledge and expertise to assess your specific circumstances and provide tailored recommendations for the optimal orientation of your greenhouse.
Collaborating with Architects, Engineers, and Agricultural Specialists
Collaborating with professionals throughout the planning and construction process can greatly enhance the success of your greenhouse. Architects can help design a structurally sound and aesthetically pleasing greenhouse, while engineers can provide expertise in areas such as foundation design and structural integrity. Agricultural specialists can offer valuable insights into crop requirements and optimal growing conditions. By working together with these experts, you can ensure that your greenhouse is positioned in the best possible way to maximize productivity and achieve your gardening goals.
In conclusion, choosing the optimal orientation for a greenhouse requires careful consideration of various factors. Sunlight exposure, wind direction, climate, terrain, existing structures, access, and visibility all play crucial roles in determining the success and efficiency of your greenhouse operation. By carefully evaluating these factors and seeking professional advice when needed, you can position your greenhouse in a way that maximizes natural resources, minimizes environmental impacts, and provides the ideal growing conditions for your plants. With the right orientation, your greenhouse can become a thriving and productive space where you can cultivate a wide range of plants throughout the year.
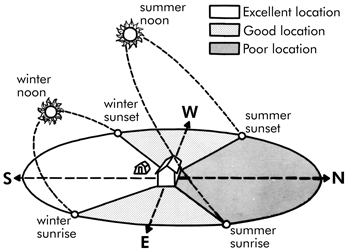
This image is property of secure.caes.uga.edu.

