
If you’ve ever dreamed of cultivating plump, juicy tomatoes in your very own greenhouse, then you’ve come to the right place! In this article, we will explore the ideal temperature for growing tomatoes in a greenhouse and uncover the secrets to a bountiful harvest. From the germination stage to the final ripening, maintaining the perfect temperature is key to unlocking the full potential of your tomato plants. So sit back, grab your notebook, and get ready to learn all about the science behind creating the perfect tomato-growing environment.

This image is property of www.allotment-garden.org.
Choosing the Right Temperature for Tomato Growth
Growing tomatoes in a greenhouse allows you to have greater control over the growing environment, including temperature. Understanding the optimal temperature range for tomato growth is crucial for maximizing your harvest and ensuring healthy plants. When considering temperature requirements for tomatoes, it’s essential to consider variations in tomato varieties and the different stages of tomato growth. By adequately controlling greenhouse temperature and adapting it to seasonal changes, you can support optimal tomato growth and avoid temperature-related issues.
Understanding the Optimal Temperature Range
Tomatoes thrive within a relatively narrow temperature range, typically between 70°F and 85°F (21°C and 29°C). Within this range, tomato plants can perform key physiological functions efficiently, such as photosynthesis, nutrient uptake, and fruit development. Temperatures below or above this optimal range can adversely affect tomato growth and yield.
Considering Variations in Tomato Varieties
It’s important to note that different tomato varieties have varying temperature preferences. Some tomato varieties are more tolerant of cooler temperatures, while others prefer warmer conditions. Therefore, when choosing tomato varieties for greenhouse cultivation, consider their specific temperature requirements to ensure that they can thrive in your greenhouse environment.
Factoring in Seedling vs. Mature Tomato Plants
Temperature requirements also vary depending on the stage of tomato growth. Seedlings, for instance, require slightly higher temperatures for successful germination and early development. As seedlings mature into fully grown tomato plants, the optimal temperature range may shift slightly. It’s essential to understand these temperature variations to provide the right conditions for each growth stage.

This image is property of drygair.com.
Temperature Requirements at Different Stages of Tomato Growth
Understanding the temperature requirements of tomatoes at each growth stage is crucial for maintaining optimal growth and ensuring a bountiful harvest. Let’s explore the ideal temperature ranges for germination, seedling development, flowering and fruit set, and fruit ripening.
Ideal Temperature for Germination
To achieve successful germination, tomato seeds require a consistent temperature between 70°F and 80°F (21°C and 27°C). This temperature range provides the necessary warmth for the seeds to break their dormancy and initiate the germination process. Ensure that the temperature remains within this range until seedlings emerge.
Temperature for Seedling Development
Once the tomato seeds have germinated, the ideal temperature range for seedling development is slightly cooler, around 65°F to 70°F (18°C to 21°C). This temperature range promotes healthy growth and enables seedlings to develop sturdy stems and well-formed leaves. Maintaining a slightly lower temperature during this stage helps prevent leggy seedlings.
Optimum Temperature for Flowering and Fruit Set
When tomato plants begin to flower, they require warmer temperatures to facilitate proper pollination and fruit set. Maintaining a temperature range of 70°F to 75°F (21°C to 24°C) during the flowering stage enhances the chances of successful pollination and the formation of healthy fruit.
Temperature Considerations during Fruit Ripening
As tomatoes transition from the flowering stage to fruit ripening, the temperature requirements change once again. For optimal fruit ripening, the temperature should be around 75°F to 85°F (24°C to 29°C). This temperature range encourages the development of flavorful and fully mature tomatoes.
Controlling Greenhouse Temperature
One of the primary advantages of greenhouse cultivation is the ability to regulate and control temperature. Here are some key strategies for effectively managing greenhouse temperature:
Utilizing Heating Systems
In colder climates or during colder seasons, greenhouse heating systems become essential for maintaining the ideal temperature range. Options such as radiant heaters, hot water systems, or forced air heaters can provide the necessary heat to keep tomato plants thriving.
Importance of Ventilation and Air Circulation
Proper ventilation plays a crucial role in regulating greenhouse temperature. By allowing the exchange of air, fresh oxygen is provided to the plants, and excess heat is released. Consider installing ventilation systems such as fans or vents to maintain optimal airflow and prevent heat buildup.
Using Shading Techniques to Regulate Temperature
In regions with scorching summers or high heat, shading techniques can be employed to prevent excessive heat accumulation within the greenhouse. Shade cloths or shading paints can be used to reduce sunlight penetration and protect tomato plants from being exposed to detrimental high temperatures.
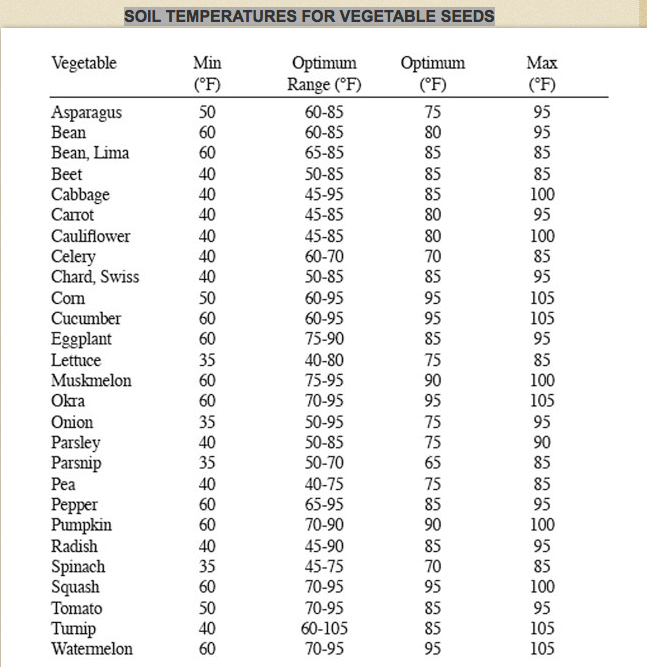
This image is property of giantveggiegardener.files.wordpress.com.
The Role of Daytime and Nighttime Temperatures
Temperature fluctuations between day and night, known as diurnal temperature variation, can significantly impact tomato growth. It’s important to understand and manage both daytime and nighttime temperatures to ensure optimal conditions for the plants.
Understanding Diurnal Temperature Variation
Diurnal temperature variation refers to the difference between the highest temperature during the day and the lowest temperature during the night. These fluctuations can have varying effects on tomato plants, depending on the stage of growth and the specific temperature range.
Balancing Optimal Temperatures during the Day and Night
Tomato plants benefit from warmer temperatures during the day, as this promotes photosynthesis and growth. However, it’s crucial to maintain cooler temperatures during the night to promote proper rest and prevent stress on the plants. Striking a balance between daytime and nighttime temperatures is key to ensuring healthy tomato growth.
The Impact of Temperature Fluctuations on Tomato Growth
Significant temperature fluctuations, especially rapid changes, can stress tomato plants and affect their overall health and productivity. Sudden drops in temperature can lead to chilling injury or frost damage, while extreme heat can cause heat stress and reduce fruit quality. Monitoring and minimizing temperature fluctuations is essential for maintaining optimal conditions.
Effects of Temperature Extremes on Tomato Plants
Understanding the effects of temperature extremes on tomato plants helps you identify potential risks and take appropriate measures to mitigate damage. Whether facing high or low temperatures, it’s crucial to be aware of the consequences and address any related issues promptly.
The Risks of High Temperatures
High temperatures can cause various adverse effects on tomato plants. Excessive heat can lead to blossom drop, reduced fruit set, and negatively impact fruit quality. Additionally, high temperatures can reduce the effectiveness of pollination, leading to poor yields.
Consequences of Low Temperatures
Cold temperatures can also pose risks to tomato plants, particularly if they fall below the recommended temperature range for tomato growth. Cold snaps can result in stunted growth, reduced fruit production, and increased susceptibility to diseases and pests. It’s important to protect tomato plants from frost or freezing temperatures using insulation or heating systems.
Addressing Potential Damage and Stress in Tomatoes
If tomato plants experience temperature-related damage or stress, it’s crucial to take appropriate actions to mitigate the effects. Providing extra care, such as providing shading, adjusting ventilation, or using protective covers, can help alleviate stress and aid in the recovery of tomato plants.

This image is property of krostrade.co.uk.
Adapting Temperature for Seasonal Changes
Seasonal changes bring about varying temperature conditions that require different approaches to maintain optimal greenhouse temperatures. Let’s explore how you can adapt temperature management during spring planting, managing summer heat, and overcoming winter cold snaps.
Optimizing Temperature for Spring Planting
In early spring, when temperatures are still relatively cool, providing supplemental heat in the greenhouse is vital for the successful establishment of tomato seedlings. Utilize heating systems and insulation to create a warm and favorable environment for germination and early growth.
Managing Summer Heat in the Greenhouse
During the scorching heat of summer, it’s essential to implement strategies to prevent excessive heat buildup in the greenhouse. Ensure proper ventilation, shading, and cooling measures are in place to maintain the ideal temperature range and protect tomato plants from heat stress.
Overcoming Cold Snaps in Winter Conditions
In winter, when temperatures drop significantly below the desired range, greenhouse heating becomes crucial for maintaining optimal conditions. Insulation and heating systems should be used to protect tomato plants from frost and freezing temperatures, ensuring their survival and continued growth.
Monitoring and Adjusting Temperature
Monitoring temperature is a critical aspect of successful greenhouse tomato cultivation. By regularly assessing temperature levels and making adjustments accordingly, you can maintain optimal growing conditions and promptly address any temperature-related issues that arise.
Using Thermometers and Sensors
Installing thermometers or temperature sensors throughout the greenhouse allows you to monitor temperature levels accurately. Place them at different heights and locations to obtain a comprehensive understanding of temperature distribution within the growing area.
Analyzing and Responding to Temperature Data
Regularly record and analyze temperature data to identify patterns, trends, and potential anomalies. By observing temperature fluctuations and patterns, you can make informed decisions about adjusting temperature management strategies to optimize growing conditions for your tomatoes.
Implementing Automatic Climate Control Systems
For precise and efficient temperature control, consider using automatic climate control systems. These systems utilize sensors and algorithms to regulate temperature, ventilation, and other environmental factors automatically. They can offer a more hands-off approach to maintaining greenhouse temperatures, allowing you to focus on other essential aspects of tomato cultivation.

This image is property of plantura.garden.
Best Practices for Maintaining Stable Temperature
Adopting best practices for maintaining stable greenhouse temperatures can help mitigate temperature-related challenges and create a favorable environment for tomato plants to thrive. Consider the following practices to ensure optimal temperature management:
Avoiding Sudden Temperature Swings
Extreme temperature swings, particularly rapid shifts, can stress tomato plants. Avoid sudden temperature changes by gradually adjusting temperatures when necessary. Sudden shifts can shock the plants and lead to adverse effects on growth and yield.
Implementing Proper Insulation
Efficient insulation is vital for preventing heat loss during colder periods and heat gain during hot seasons. Insulate the greenhouse walls, ceiling, and flooring to reduce temperature variations and create a more stable growing environment for your tomatoes.
Controlling Humidity Levels
In addition to temperature, humidity levels also affect tomato growth. High humidity can impede pollination and create a favorable environment for diseases, while low humidity can lead to excessive water loss and stress on the plants. Ensure proper ventilation, use humidifiers or dehumidifiers as necessary, to maintain optimal humidity levels.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Despite your best efforts, you may encounter temperature-related issues while growing tomatoes in a greenhouse. Here are some common issues and potential remedies to address these challenges:
Dealing with Heat Stress in Tomato Plants
Heat stress can occur during periods of extreme heat, leading to wilted, scorched, or sunburnt foliage. Provide ample shading, increase ventilation, and keep the greenhouse well-ventilated to mitigate heat stress. Applying a protective foliar spray can also help reduce heat-related damage.
Identifying and Remedying Cold-Related Problems
Cold-related problems can manifest as leaf discoloration, stunted growth, or frost damage. Insulate the greenhouse adequately, use heating systems, and consider row covers or frost blankets to protect tomato plants from cold snaps. Providing a heat source or using soil warming mats can also help maintain favorable root temperatures.
Resolving Temperature-related Diseases and Disorders
Temperature fluctuations can contribute to the development of specific diseases and disorders, such as blossom end rot or fruit cracking. Maintain stable temperature and humidity levels, avoid extreme fluctuations, and ensure proper nutrient management to minimize the occurrence of temperature-related issues.
Conclusion
Choosing the right temperature for growing tomatoes in a greenhouse is essential for promoting healthy growth, maximizing yields, and preventing temperature-related issues. By understanding the optimal temperature range, considering variations in tomato varieties, and factoring in the different stages of tomato growth, you can provide the best possible growing environment for your tomato plants. Implementing effective temperature control strategies, adapting to seasonal changes, and monitoring and adjusting temperature as needed are key to ensuring successful greenhouse tomato cultivation. With careful attention to temperature management, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious and healthy tomatoes from your greenhouse.

