
Have you ever wondered what a cold frame greenhouse is and what purpose it serves? A cold frame greenhouse is a unique structure that acts as a protective environment for plants, shielding them from harsh weather conditions and extending the growing season. It essentially works as an insulated box with a transparent lid, harnessing the power of the sun to create a warmer microclimate for your plants. Let’s explore the various functions of a cold frame greenhouse and how it can be a valuable addition to your gardening endeavors.
What is a Cold Frame Greenhouse?
A cold frame greenhouse is a miniature greenhouse used to extend the growing season, protect plants from frost, harden off seedlings, create a microclimate, and grow cold-hardy vegetables. It is a simple structure with a transparent covering that allows sunlight to reach the plants while providing some insulation and protection from harsh weather conditions. Cold frame greenhouses are popular among gardeners and small-scale farmers as they are affordable, easy to construct, and versatile in their applications.
The Purpose of a Cold Frame Greenhouse
Extending the Growing Season
One of the primary purposes of a cold frame greenhouse is to extend the growing season. By creating a controlled environment, you can start planting and growing crops earlier in the spring and continue harvesting well into the fall or even winter months. This is particularly beneficial in regions with shorter growing seasons or colder climates.
Protecting Plants from Frost
Cold frame greenhouses offer protection to delicate plants by shielding them from frost and extreme cold temperatures. The greenhouse structure traps heat from sunlight, creating a warmer environment inside which helps prevent frost damage. This is particularly useful in early spring when frost is still a common occurrence or during sudden temperature drops in colder regions.
Hardening off Seedlings
Seedlings, especially those started indoors, need to be gradually exposed to outdoor conditions before being transplanted into the garden. Cold frame greenhouses provide an ideal space for hardening off seedlings. By gradually opening the greenhouse lid and allowing them to experience the outdoor elements, you can ensure that the seedlings adapt to the harsher conditions and have a better chance of survival outside.
Creating a Microclimate
Cold frame greenhouses create a microclimate that differs from the surrounding outdoor environment. The structure acts as a barrier against wind and excessive precipitation, providing a more sheltered and controlled space for plants to grow. This makes it possible to grow plants that may not typically thrive in your particular climate or grow them earlier in the season than would normally be possible.
Growing Cold-Hardy Vegetables
Cold frame greenhouses are particularly popular for growing cold-hardy vegetables. Vegetables like lettuce, spinach, kale, and carrots can withstand cooler temperatures and even thrive in frosty conditions. With the help of a cold frame greenhouse, you can enjoy a fresh supply of homegrown produce even during the colder months when traditional outdoor gardening may not be possible.
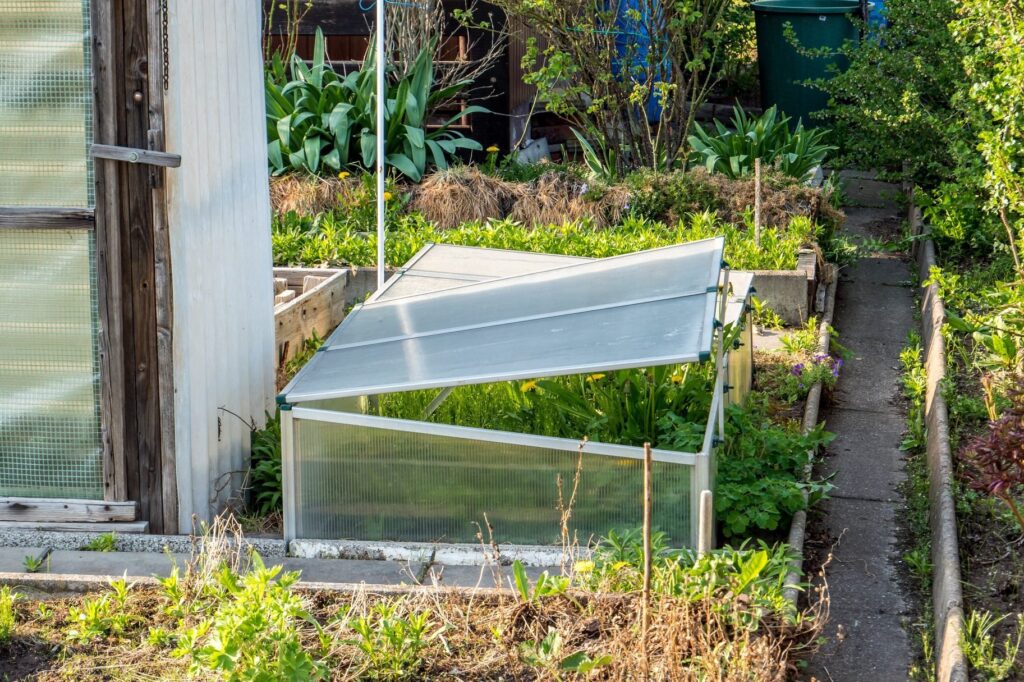

This image is property of www.familyhandyman.com.
Components of a Cold Frame Greenhouse
Frame and Structure
The frame of a cold frame greenhouse can be made from various materials such as wood, PVC pipes, or metal. It provides the structural support for the entire greenhouse and must be stable and durable. The frame can be built in different shapes and sizes, depending on your preferences and available space.
Covering Material
The covering material of a cold frame greenhouse should be transparent to allow sunlight to reach the plants. Common options include glass, polycarbonate sheets, or clear plastic. Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of insulation, durability, and cost. Consider the climate and the specific needs of your plants when choosing the covering material.
Ventilation and Temperature Control
Proper ventilation is crucial within a cold frame greenhouse to prevent overheating and ensure air circulation. Ventilation is typically achieved through adjustable lids or hinged panels that can be opened or closed as needed. By regulating airflow, you can maintain optimal temperature and control humidity levels inside the greenhouse.
Insulation
To provide additional insulation and protect plants during colder periods, you can insulate the sides or even the top of the cold frame greenhouse. This can be done using materials such as straw bales, bubble wrap, or insulation panels. Insulation helps to retain heat and keep the interior temperature more stable, providing extra protection against frost and cold snaps.
Foundation
A solid foundation is important for the stability and durability of a cold frame greenhouse. It helps level the greenhouse, prevent soil erosion, and ensure proper drainage. Depending on the type of frame and the size of the greenhouse, the foundation can be as simple as a level and compacted soil base or more elaborate options like concrete or raised beds.
Choosing the Right Location
Sun Exposure
When selecting the location for your cold frame greenhouse, it is crucial to consider sun exposure. Choose a spot that receives ample sunlight throughout the day, especially during the colder months when sunlight is more limited. A southern or southeastern exposure is ideal for maximizing sunlight exposure and ensuring proper plant growth.
Drainage
Good drainage is essential to prevent waterlogging and excess moisture around the plants. Avoid low-lying areas where water tends to accumulate or locations with poor soil drainage. If necessary, you can improve the drainage by incorporating gravel or installing drainage pipes around the perimeter of the cold frame greenhouse.
Proximity to Water and Electricity
Consider the accessibility of water and electricity when choosing the location for your cold frame greenhouse. Having a water source nearby makes watering easier and more convenient, while access to electricity allows for the installation of heaters or other climate control devices if needed. However, if water and electricity are not readily available, alternative solutions can be found.
Protection from Wind and Animals
Find a location that offers some natural protection against strong winds that can potentially damage the structure or cause excessive cooling. Placing the cold frame greenhouse near a building or a windbreak, such as trees or fences, can help shield it from strong gusts. Additionally, consider protection from animals, such as rabbits or deer, by choosing a location less accessible to them or installing fencing around the greenhouse.
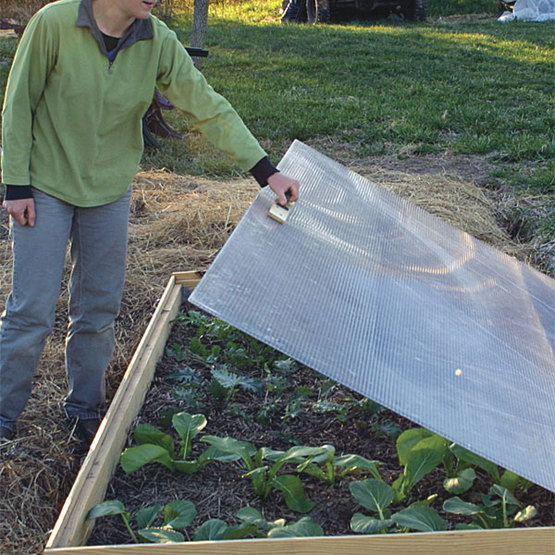

This image is property of images.finegardening.com.
Preparing the Site
Clearing the Area
Before setting up your cold frame greenhouse, clear the area of any debris, rocks, or vegetation. Remove any obstacles that may interfere with the construction process or restrict the growth of plants inside the greenhouse. Clearing the area also allows for better visibility and ensures a clean and organized space for your greenhouse.
Leveling the Ground
Level the ground where the cold frame greenhouse will be placed to create a stable and even surface. This can be done by removing excess soil or adding soil to low areas, as well as using a level tool to check for evenness. A level ground helps with proper drainage and ensures that the greenhouse sits securely and evenly on the surface.
Adding Organic Matter
Incorporate organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, into the soil to improve its fertility and nutrient content. This promotes healthier plant growth and enhances the overall productivity of the greenhouse. Organic matter also helps with moisture retention and provides a more favorable growing environment for your plants.
Creating a Base
Consider creating a base for your cold frame greenhouse to provide additional stability and support. This can be done using materials such as concrete, wooden beams, or even raised beds. A solid base not only helps anchor the greenhouse but also prevents soil erosion and enhances the overall longevity of the structure.
Building a Cold Frame Greenhouse
Selecting a Design
Choose a design for your cold frame greenhouse that suits your needs, available space, and budget. There are various design options, from simple and basic structures to more complex ones with added features. Consider factors such as the desired size, shape, and materials when selecting the design that will work best for your gardening endeavors.
Materials and Tools
Gather all the necessary materials and tools before beginning the construction process. This may include framing materials, screws or nails, coverings, hinges, tools like a saw, hammer, screwdrivers, and a measuring tape. Make sure to have everything on hand to ensure a smooth and efficient building process.
Constructing the Frame
Start by constructing the frame of the cold frame greenhouse according to your chosen design. Follow the plans or instructions carefully, ensuring that the frame is secure and stable. Ensure that the corners are square and that the frame is level and plumb. This will serve as the foundation for the rest of the structure.
Attaching the Covering Material
Once the frame is complete, proceed to attach the chosen covering material to the structure. This may involve securing glass panels, polycarbonate sheets, or plastic coverings to the frame. Take care to ensure a tight and secure fit, as this will prevent drafts and help retain heat inside the greenhouse.
Setting up Ventilation
Install the ventilation system according to the design and specifications of your cold frame greenhouse. This may involve creating adjustable lids, hinged panels, or vents that can be opened or closed as needed. Proper ventilation is essential for regulating temperature and preventing overheating or excessive humidity.
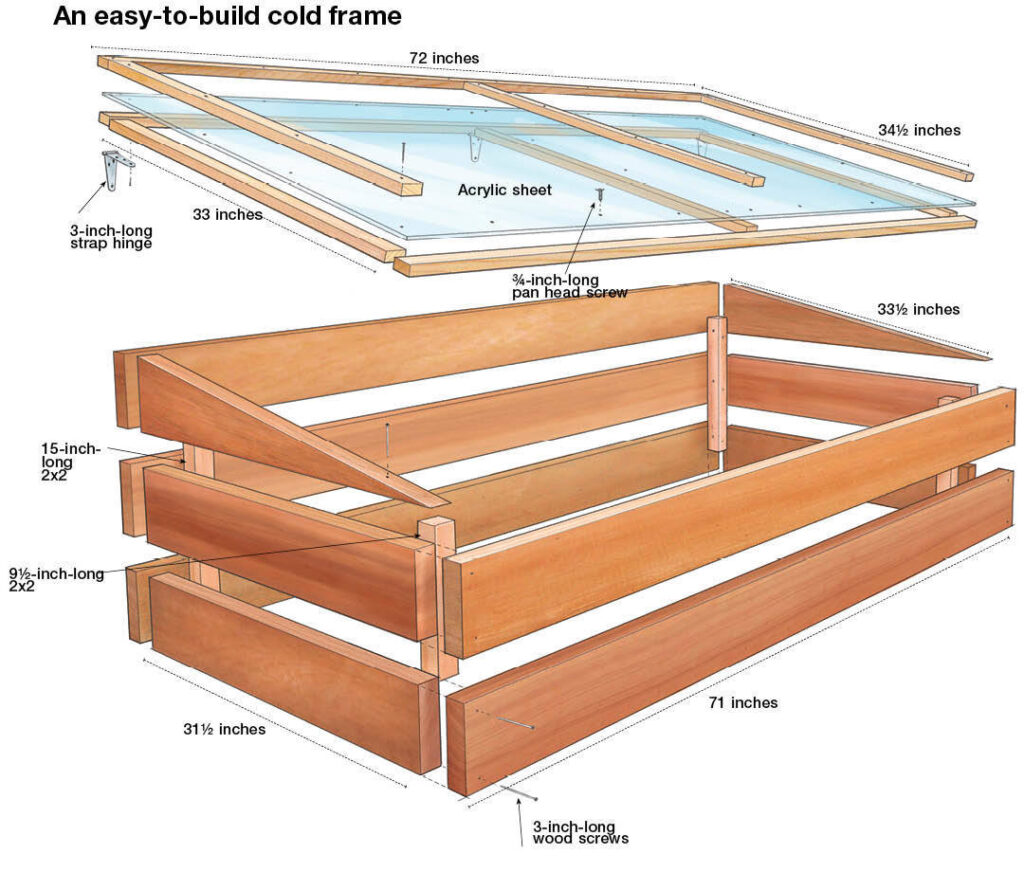
This image is property of images.finegardening.com.
Maintaining a Cold Frame Greenhouse
Watering
Regular and adequate watering is crucial for the health and growth of plants inside a cold frame greenhouse. Monitor the soil moisture levels and water as needed, taking care not to overwater or allow the soil to become waterlogged. Consider using a drip irrigation system or a watering can with a fine spray nozzle to ensure even and gentle watering.
Temperature Management
Maintaining proper temperature levels is essential in a cold frame greenhouse. Monitor the temperature regularly and make adjustments as needed. In colder weather, consider using additional insulation or heating devices to prevent frost damage. During warmer periods, ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating.
Pest and Disease Control
Just like any other garden, a cold frame greenhouse is susceptible to pests and diseases. Regularly inspect your plants for any signs of pests or diseases and take appropriate measures to control and prevent their spread. This may involve using organic pest control methods, such as handpicking or introducing beneficial insects, or using natural fungicides to combat diseases.
Cleaning and Sanitizing
Keep your cold frame greenhouse clean and sanitary to prevent the buildup of pests, diseases, and debris. Regularly remove fallen leaves, dead plants, and any other organic material that can harbor pests or pathogens. Wash the interior and exterior of the greenhouse periodically with a mild disinfectant or soapy water to maintain a healthy growing environment.
Types of Plants to Grow in a Cold Frame Greenhouse
Cool-Season Crops
Cold frame greenhouses are excellent spaces for growing cool-season crops such as lettuce, spinach, radishes, and kale. These crops thrive in colder temperatures and can be harvested earlier in the season or even throughout the winter with the help of a cold frame greenhouse.
Root Vegetables
Root vegetables, such as carrots, beets, and turnips, also do well in a cold frame greenhouse. They appreciate the insulating properties of the greenhouse and can be harvested even as the ground freezes. The controlled environment allows for longer growing seasons and sweeter, more flavorful root crops.
Ornamental Plants
Cold frame greenhouses can also be used to grow a variety of ornamental plants. Flowers and plants that require a slightly warmer environment than the outdoors can be successfully cultivated in a cold frame greenhouse. The controlled conditions allow for greater experimentation and diversity in your garden.
Seed Starting
Starting seeds indoors is a common practice, and a cold frame greenhouse provides an excellent space to do so. The greenhouse offers protection and warmth during the crucial germination and early growth stages of seedlings. With proper care and temperature management, you can get a head start on your garden by starting seeds in a cold frame greenhouse.

This image is property of www.shelterlogic.com.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Condensation and Humidity
One common challenge in a cold frame greenhouse is condensation and excessive humidity. Excessive moisture can lead to fungal diseases or rot. To mitigate this, ensure proper ventilation to allow for airflow and reduce condensation. Adding a layer of gravel or pebbles at the base of the greenhouse can help absorb excess moisture.
Temperature Fluctuations
Temperature fluctuations can pose challenges in a cold frame greenhouse, especially during extreme weather conditions. To maintain a more stable temperature, consider using additional insulation or providing supplemental heating during colder periods. Likewise, on hot days, ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating.
Wind Damage
Strong winds can potentially damage or even destroy a cold frame greenhouse. To minimize this risk, ensure that your greenhouse is securely anchored to the ground and positioned in a location that offers some natural wind protection, such as near a building or windbreak. Additionally, reinforcing the greenhouse structure with sturdy materials can help withstand strong gusts.
Pest Infestations
Pests can find their way into your cold frame greenhouse, especially if it is not properly sealed or maintained. Regular inspection and proactive pest control measures are essential to prevent infestations. Consider using organic pest control methods, such as introducing beneficial insects or companion planting, to reduce pests’ impact on your plants.
Conclusion
A cold frame greenhouse is a versatile and valuable addition to any garden or small-scale farm. By extending the growing season, protecting plants from frost, and creating a controlled microclimate, a cold frame greenhouse allows you to grow a wider variety of plants and enjoy fresh produce year-round. With careful planning, proper construction, and regular maintenance, a cold frame greenhouse can help you maximize your gardening efforts and achieve greater success in your plant-growing endeavors.

This image is property of greenhouseemporium.com.

