
In your quest to create the perfect environment for your greenhouse, one crucial factor cannot be overlooked: temperature. Finding the ideal temperature for your greenhouse can make all the difference in the success of your plants’ growth. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, understanding the importance of maintaining the right temperature is key to nurturing healthy and thriving plants. In this article, we will explore the significance of temperature control in a greenhouse and provide insights on finding the ideal temperature to create an optimal microclimate for your plants.

This image is property of nutricontrol.com.
Factors Affecting Greenhouse Temperature
Location
The location of a greenhouse plays a significant role in determining its temperature. Factors such as latitude, altitude, and proximity to bodies of water can greatly influence the amount of sunlight and heat that a greenhouse receives. Greenhouses located in higher latitudes or altitudes generally experience cooler temperatures, while those closer to the equator may receive more intense sunlight and higher temperatures. Additionally, greenhouses located near large bodies of water may benefit from the moderating effect of the water, resulting in more stable temperatures.
Season
The time of year has a major impact on greenhouse temperatures. During the winter months, when the days are shorter and sunlight is less abundant, greenhouse temperatures can drop significantly. Conversely, in the summer, when days are longer and the sun is stronger, temperatures can rise to uncomfortably high levels. It is crucial to monitor and adjust temperature control measures accordingly to ensure optimal growing conditions for greenhouse plants throughout the different seasons.
Time of Day
The time of day also affects greenhouse temperatures. In general, greenhouse temperatures tend to be lowest in the early morning and highest in the late afternoon. This fluctuation is due to the daily variation in sunlight intensity and ambient temperature. It is important to consider these temperature changes when selecting and implementing temperature management strategies.
Temperature Requirements for Different Greenhouse Purposes
Seed Germination
For seed germination, maintaining a consistent and slightly elevated temperature is crucial. Most seeds germinate best within a temperature range of 65 to 75 degrees Fahrenheit (18 to 24 degrees Celsius). This warmth is necessary to kickstart the germination process and promote healthy seedling development.
Vegetative Growth
During the vegetative growth stage, when plants focus on developing foliage and stems, a slightly higher temperature is typically needed. The optimal temperature range for vegetative growth is usually between 70 and 80 degrees Fahrenheit (21 to 27 degrees Celsius). Providing the right temperature encourages vigorous growth and helps plants build a strong foundation for future stages of development.
Flowering and Fruit Production
As plants transition into the flowering and fruiting stage, temperature requirements may vary depending on the specific crop. However, in general, most greenhouse crops thrive when temperatures range from 65 to 75 degrees Fahrenheit (18 to 24 degrees Celsius) during the day, and slightly cooler temperatures, between 60 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit (15 to 21 degrees Celsius), at night. These temperatures promote optimal flower development, pollination, and fruit set, leading to better yields and quality.
Optimal Temperature Ranges for Common Greenhouse Crops
Tomatoes
Tomatoes are one of the most popular greenhouse crops, and they generally prefer higher temperatures for optimal growth. During the day, the ideal temperature range for tomatoes is between 70 and 85 degrees Fahrenheit (21 to 29 degrees Celsius). At night, temperatures should range from 60 to 70 degrees Fahrenheit (15 to 21 degrees Celsius).
Lettuce
Lettuce is a cool-season crop that thrives in slightly lower temperatures compared to other greenhouse crops. During the day, temperatures between 60 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit (15 to 21 degrees Celsius) are ideal for lettuce. At night, temperatures should range from 55 to 65 degrees Fahrenheit (13 to 18 degrees Celsius).
Cucumbers
Cucumbers are warm-season crops that require higher temperatures, similar to tomatoes. The optimal daytime temperature range for cucumbers is between 75 and 85 degrees Fahrenheit (24 to 29 degrees Celsius), with nighttime temperatures ranging from 65 to 70 degrees Fahrenheit (18 to 21 degrees Celsius).
Peppers
Peppers are also warm-season crops that prefer higher temperatures. During the day, peppers thrive in temperatures between 70 and 85 degrees Fahrenheit (21 to 29 degrees Celsius). At night, temperatures should range from 65 to 75 degrees Fahrenheit (18 to 24 degrees Celsius).
Maintaining Ideal Greenhouse Temperature
Heating Methods
To maintain the ideal temperature range for greenhouse crops, various heating methods can be employed. Common options include radiant heaters, forced-air heaters, geothermal heating systems, and hot water or steam systems. The choice of heating method depends on factors such as cost, energy efficiency, and the specific heating requirements of the crops being grown.
Cooling Methods
In warmer climates or during the summer months, cooling methods are crucial to prevent the greenhouse from overheating. Popular cooling methods include natural ventilation, shading, evaporative cooling systems, and misting systems. These methods help reduce the temperature inside the greenhouse and maintain optimal growing conditions.
Ventilation
Proper ventilation is essential for controlling greenhouse temperature and humidity levels. Ventilation systems, such as exhaust fans, sidewall vents, and roof vents, allow for air exchange to regulate temperature and remove excess humidity. Adequate airflow also helps prevent the buildup of pests and diseases, ensuring a healthy growing environment for greenhouse plants.

This image is property of i0.wp.com.
Monitoring and Control of Greenhouse Temperature
Thermostats
Thermostats are indispensable tools for monitoring and controlling greenhouse temperature. They provide accurate temperature readings and allow growers to set desired temperature ranges. When the temperature reaches a certain threshold, the thermostat triggers the heating or cooling system to maintain the desired temperature.
Temperature Sensors
Temperature sensors are used to gather real-time temperature data from various locations within the greenhouse. This data helps identify temperature variations and potential hot or cold spots. Using temperature sensors strategically allows for precise temperature management.
Automated Systems
Automated systems offer a convenient and efficient way to monitor and control greenhouse temperature. These systems integrate thermostats, temperature sensors, and other environmental controls to automate temperature adjustments. With customizable settings, growers can ensure that the greenhouse maintains the desired temperature range without constant manual intervention.
Effects of Temperature Variations on Greenhouse Plants
Growth Stimulation
Temperature variations can have different effects on greenhouse plants depending on the crops and growth stage. In some cases, slight variations in temperature can stimulate plant growth by triggering specific physiological responses. For example, cooler temperatures during flower initiation can promote better flower development and enhanced fruit set.
Growth Inhibition
On the other hand, extreme temperature variations, whether too hot or too cold, can inhibit plant growth and even lead to irreversible damage. High temperatures can cause wilting, sunscald, and reduced productivity, while low temperatures can stunt growth, delay flowering, and increase the risk of frost damage. Proper temperature management is crucial to prevent growth inhibition and maintain healthy, productive plants.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
Temperature Management Tips
Insulation
Proper insulation is paramount for minimizing temperature fluctuations and ensuring energy efficiency in the greenhouse. Insulating materials such as double-layered glazing, bubble wrap, or insulating curtains can help retain heat during colder periods and provide a barrier against excessive heat during warmer periods. Well-insulated greenhouses provide a more stable temperature environment for optimal plant growth.
Shading
During periods of intense sunlight or high temperatures, shading is essential to protect greenhouse plants from excessive heat and light. Applying shading materials, such as shade cloth or whitewash, can reduce the amount of sunlight reaching the plants, preventing overheating and potential sun damage. Shading techniques should be adjusted as needed to maintain the desired temperature range.
Air Circulation
Promoting air circulation within the greenhouse helps distribute heat evenly and reduces the risk of hot or cold spots. This can be achieved by using fans, natural ventilation, or a combination of both. Good air circulation improves temperature uniformity and helps prevent the buildup of disease-causing pathogens.
Cool-season vs. Warm-season Greenhouse Crops
Differences in Temperature Requirements
Cool-season and warm-season greenhouse crops have distinct temperature requirements. Cool-season crops, such as lettuce and some herbs, prefer lower temperatures and can tolerate cooler conditions. Warm-season crops, like tomatoes and peppers, require higher temperatures and are less tolerant of cold temperatures. Understanding these differences is crucial for successfully growing a variety of crops in a greenhouse environment.
Suitable Temperature Ranges
Cool-season crops generally thrive within a temperature range of 55 to 70 degrees Fahrenheit (13 to 21 degrees Celsius) during the day, and slightly cooler temperatures, between 45 and 55 degrees Fahrenheit (7 to 13 degrees Celsius), at night. Warm-season crops, on the other hand, typically prefer daytime temperatures between 70 and 85 degrees Fahrenheit (21 to 29 degrees Celsius), and nighttime temperatures ranging from 65 to 75 degrees Fahrenheit (18 to 24 degrees Celsius).

This image is property of img.hobbyfarms.com.
Potential Challenges in Maintaining Greenhouse Temperature
Extreme Weather Events
Extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, cold snaps, or sudden temperature fluctuations, can pose challenges in maintaining greenhouse temperature. These events can stress plants, affect growth, and even lead to crop losses. To mitigate these challenges, it is important to have backup heating and cooling systems in place, as well as monitoring tools to detect and respond to temperature changes.
Equipment Malfunctions
Unforeseen equipment malfunctions, such as heater or cooling system failures, can have a significant impact on greenhouse temperature. Regular maintenance, inspection, and having spare equipment on hand can help mitigate the risk of equipment failure and ensure prompt repairs or replacements if needed.
Pest and Disease Outbreaks
Temperature variations can also impact the risk of pest and disease outbreaks in the greenhouse. Fluctuating temperatures can weaken plants and make them more susceptible to pests and diseases. Implementing integrated pest management practices, maintaining proper sanitation, and regularly monitoring plant health can help prevent and address any potential issues.
Conclusion
Maintaining the ideal temperature in a greenhouse is vital for creating an optimal growing environment and ensuring the successful cultivation of various crops. Factors such as location, season, and time of day significantly affect greenhouse temperature. Understanding the temperature requirements for different purposes and crops, as well as implementing appropriate heating, cooling, and ventilation methods, is key to achieving optimal growth and maximizing yields. By monitoring and controlling greenhouse temperature, addressing temperature variations, and implementing effective temperature management strategies, growers can create a thriving and productive greenhouse environment.
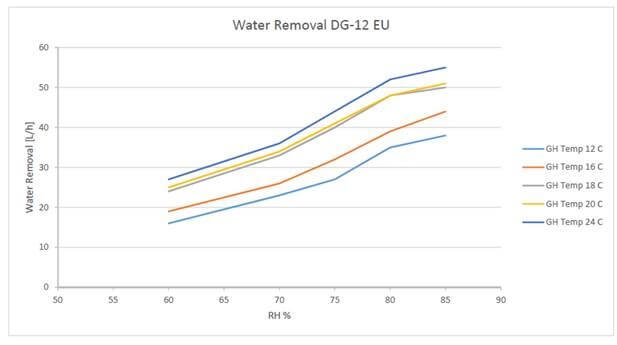
This image is property of drygair.com.

